What are the Different Parts of a Boat Called? (A Complete Guide)
Whether you’re new to boating or a veteran captain, it’s important to learn the basic parts of a boat and related terminology. This blog post will cover the essential parts of a boat and what they do. We’ll also discuss some basic boat terms so you can feel confident talking to other boaters.
While different boats will have slightly different parts, the basics remain the same. The information below specifically focuses on boat parts and does not include details relative to ships.
Read on for a simple breakdown of boat parts and terminology, including detailed information on how each part fits into the overall design of a vessel.
What Are the Different Areas or Sections of a Boat Called?
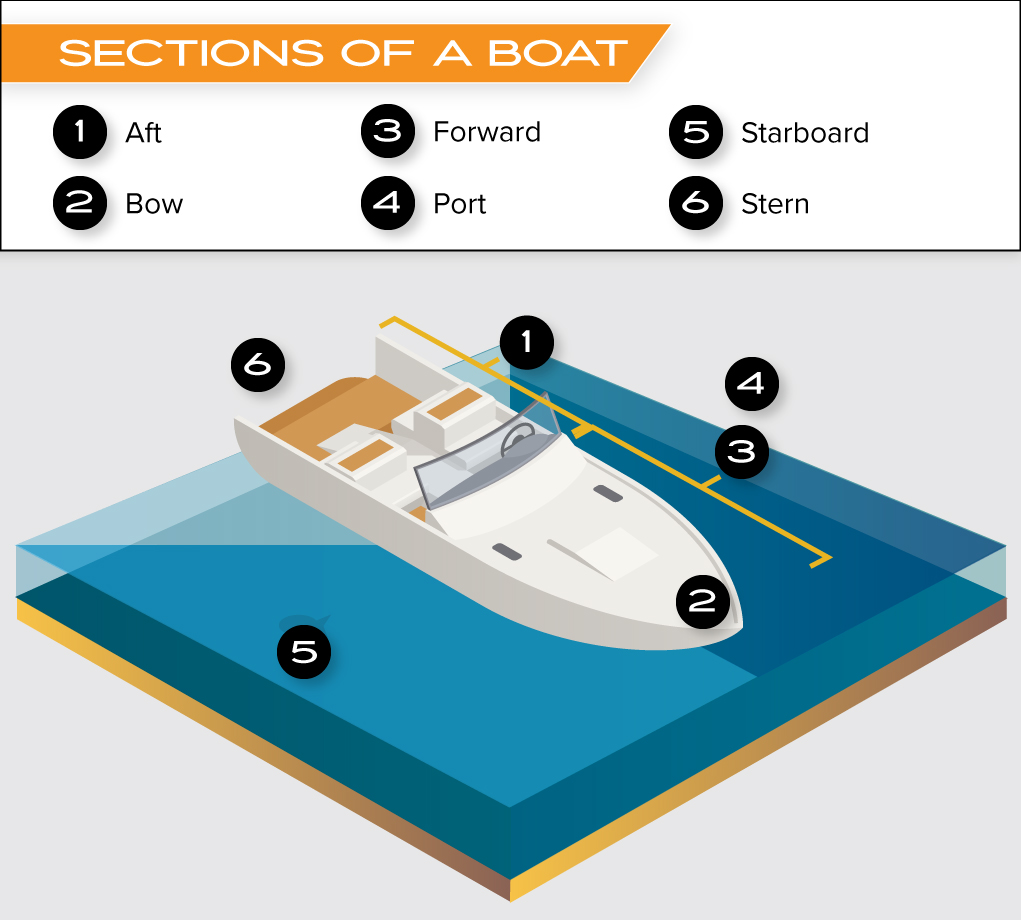
To start, we’ll focus on the areas and sections of a boat.
- Aft – Aft describes the general location near the back end of a boat or toward the stern of a vessel.
- Bow – The bow is the front end of the boat. The bow cuts through the water and provides a smooth ride for the boat and its occupants. The bow also helps to deflect waves away from the boat, which can improve its stability and prevent rollover in rough conditions.
- Forward – The area of the boat towards the front of the boat or bow.
- Port – The left side of the boat.
- Starboard – The right side of the boat
- Stern – The stern is the back end of a boat. The stern is where the engine is typically located.
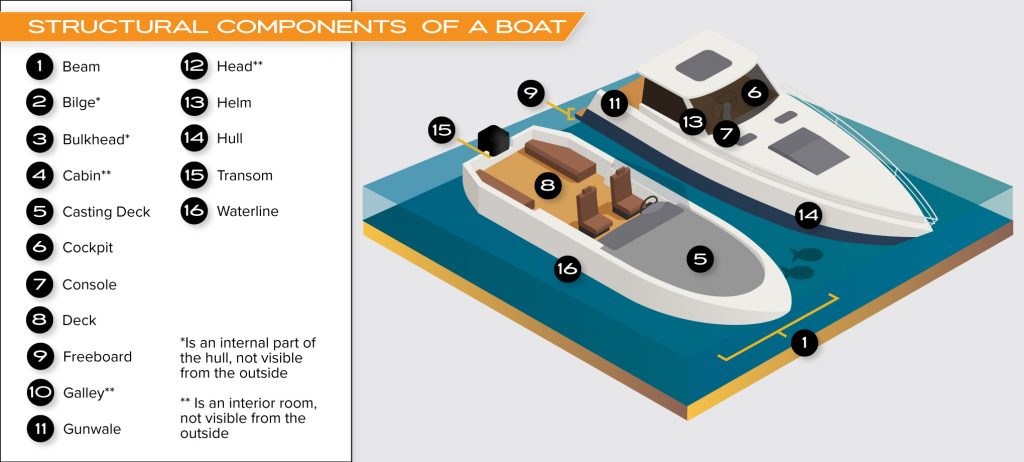
What are the Core Parts and Essential Structural Components of a Boat Called?
- Beam – The beam of a boat is its width at its widest point. For most boats, this is at the midship section. The beam plays an important role in determining the stability and carrying capacity of the vessel. A wider beam means that the boat will be more stable, but it will also require more power to move through the water. Conversely, a narrower beam will make the boat easier to maneuver, but it will be less stable.
- Bilge – The bilge is the lowest indoor space on a boat, where water and other liquids collect. The bilge pump removes water from the bilge and pumps it overboard.
- Bulkhead – A bulkhead is a wall or partition that divides a hull into compartments. Bulkheads can also provide additional strength to the hull.
- Cabin – A cabin is an enclosed space on a ship or boat, typically located below deck, where people can sleep or take shelter from the weather. They are usually equipped with basic furniture, such as beds, storage shelves, and a small table. In some cases, cabins may also have a private bathroom.
- Casting Deck – A casting deck is a platform on a boat used for fishing. It is usually located at the front of the boat. The casting deck provides a stable surface for casting.
- Cockpit – A boat’s cockpit is where the helmsman, or person steering the boat, stands. The cockpit is usually enclosed on larger boats, but the cockpit may be open on small boats. The cockpit is typically equipped with instrument panels and controls, as well as seating for the crew.
- Console – A console is an area on a boat where the captain or helmsman stands while steering. The console usually houses the boat’s controls and instruments. In some cases, the console may also be equipped with seating, storage, or other features.
- Deck – A deck is a flat surface area on a boat that typically provides space for passengers or cargo. Decks are located on the stern, bow, or midship of a vessel. Most decks are constructed from wood, fiberglass, or aluminum. Some deck features include chairs, fishing space, railings, and storage compartments.
- Freeboard – The freeboard is the distance between the main deck and the waterline of a boat. The freeboard is important because it affects the stability of the vessel and how much weight it can carry. The freeboard also determines how much wind and wave action the boat will be exposed to.
- Galley – A galley is a kitchen aboard a boat and is typically equipped with a stove, sink, and other basic amenities for food preparation.
- Gunwale – The gunwale of a boat is the upper edge of the hull, typically where the sides meet the deck. It is also sometimes referred to as the trim or molding that runs along this edge. The gunwale serves several essential functions. First, it helps to protect the boat from bumps and scrapes. Second, it provides an attachment point for various components such as railings and cleats.
- Head – A head is a room on a boat that contains a toilet and sink. It may also include a shower.
- Helm – The helm of a boat is the location from which the captain or helmsman controls the vessel. The helm includes a steering wheel, throttle, and other control levers that allow the captain to navigate the boat. In some cases, the helm may also be equipped with navigational instruments such as a compass or GPS.
- Hull – The hull is the watertight body of a ship or boat. It is the structure that floats a vessel and gives it its shape.
- Transom – The transom on a boat is the flat panel that forms the stern or back end. The transom provides both structural support and a place to mount the motor, steering system, and other hardware. In some cases, the transom also serves as a storage area or housing for the boat’s batteries in a battery compartment.
- Waterline – The waterline is the line where the boat’s hull and surface of the water meet.
What are the Operational (Functional) Parts of a Boat?
Now that we’ve described different structural parts and areas of boats, we’ll discuss parts that are useful or necessary to operate the boat.
- All Around Light – The all-around light on a boat is a white light visible in all directions. It indicates the boat’s location to other vessels. All-around lights are an essential safety feature for boats, and their proper use can help to prevent collisions and accidents.
- Bilge Pump – A bilge pump is a vital part of any boat, helping to keep the bilge (the area where water and other liquids collect) free of liquid. Bilge pumps come in a variety of sizes and styles, but all work to remove fluid from the bilge and pump it overboard. Some bilge pumps are manual, and operated by a handle. However, most are automatic, activated by a float switch, or user activated with an on/off button or switch. Bilge pumps are a crucial safety feature on boats, as they help to prevent the boat from sinking in the event of a leak or other water accumulation.
- Anchor – An anchor is a device which secures a vessel to the bottom of a body of water. The anchor chain, or rode, is connected to the anchor, and the other end is attached to the vessel. Anchors must be properly sized for the vessel and the depth of water. The anchor must also be able to hold the vessel in place in case of bad weather or strong currents.
- Bimini Top – A bimini top is a type of canopy that provides shade on a boat. The bimini top is mounted on a frame attached to the boat. The frame is usually made of aluminum or stainless steel and is covered with a fabric canopy. The bimini top can be folded down when it is not in use.
- Cleats – Boat cleats are locking devices used to tie down boats. They function by keeping a moored boat in place. The cleats are typically made out of metal and are often bolted onto the boat’s deck.
- Fenders – A fender is a bumper, usually made of rubber or plastic, placed on the side of a boat. It protects the boat from impact when docking. Fenders are essential for preventing scratches and other damage to the hull.
- Fishfinder – A fishfinder is a graph that uses electronic pulses to detect fish in the water. The graph displays the location and depth of the fish. Fishfinders can also help to identify underwater cover and structure. Most fishfinders include robust mapping capabilities with satellite overlay, contours, and other important details.
- Hardtop – A hardtop is a type of boat cover made from hard materials, such as fiberglass or aluminum. Hardtops provide a number of benefits, including protection from the sun and weather, as well as added storage space.
- Hatch – A hatch is a small door or opening that provides access to an enclosed space. Hatches are typically made of watertight materials, such as metal or fiberglass, in order to keep the space below dry.
- Hotfoot – Hotfoots are commonly found on bass boats or other high-performance boats. A hotfoot is a pedal-operated throttle similar to a gas pedal in an automobile. Depressing the pedal causes the boat to accelerate while pulling back on the pedal results in deceleration.
- Jack plate – A jack plate is a flat plate mounted on the back of a boat (transom area). The jack plate has several purposes. First, it provides a stable platform for mounting an outboard motor. Second, it can be used to adjust the position of the outboard motor, which is important for both performance and safety. Finally, the jack plates are used to raise or lower the outboard motor, providing a way to adjust the depth of the propeller in the water.
- Livewell – A livewell is a tank of aerated water that keeps bait or fish alive and in good condition. Livewells are common on fishing boats and vary in size depending on the type of boat and the intended use. Some livewells are simply recirculating systems, while others include features such as oxygenators or live baitwells. Most livewells are located in the stern of the boat, where anglers can easily access them. Some livewells also include draining systems that allow for easy and proper disposal of live bait or catch.
- Navigational Lights (Red and Green) – All boats must have navigational lights that show their position and help to avoid collisions, especially in low visibility conditions. Boats must have a red light on the port (left) side, a green light on the starboard (right) side, and a white light at the stern. Be sure to check and familiarize yourself with regulations governing the usage of navigational lights.
- PFD – Although technically not part of a boat, PFDs deserve special mention because of their vital role in safety while boating. A PFD, or personal flotation device, is a device worn by passengers on a boat. PFDs provide extra buoyancy and keep a person’s head above water in the event of an emergency.
- Propeller (A.K.A. “prop”) – A propeller is a device that provides propulsion for a boat. It consists of blades that spin in water to create thrust. The propeller is attached to the boat’s engine via a shaft. The engine powers the propeller, which in turn moves the boat through the water. Propellers come in a variety of shapes and sizes, and they can be made from different materials, such as aluminum or stainless steel.
- Rod Holder – A rod holder is a device that supports a fishing rod.
- Rub Rail – A rub rail is a narrow strip of material, typically metal, rubber, or vinyl, that runs along the edges of a boat. Its primary purpose is to protect the hull from impact..
- Safety lanyard (also known as a “kill switch”) – A safety lanyard on a boat is a cord or strap that attaches to the boat operator and can stop the engine in the event of an emergency. If the operator is thrown from the helm, safety lanyards detach from a switch and shut off engine power.
- Shallow Water Anchor -A shallow-water anchor uses a hydraulic mechanism to deploy a spike into the bottom of the body of water to keep a boat in place. Shallow water anchors can also be smaller, hand-held spikes able to be inserted by the user manually for smaller boats or kayaks.
- Swim platform/swim ladder – A swim platform is a flat, wide surface on the back of a boat that is used for swimming and sunbathing. A swim ladder is a set of steps that leads from the swim platform (where present) or back of the boat down into the water. It can help people get in and out of the water.
- Throttle – The throttle on a boat is responsible for regulating the speed of the vessel. It does this by controlling the flow of fuel to the engine. When the throttle is open, more fuel can reach the engine, increasing speed. Conversely, when the throttle is closed, less fuel is delivered to the engine, resulting in a decrease in speed. The throttle can also stop the engine altogether by cutting off the supply of fuel.
- Trolling Motor – A trolling motor is a small electric motor which can propel a boat at slow speeds. Trolling motors are not intended for primary propulsion. Instead, they are typical use is to maneuver the boat when fishing at slow speeds.
- VHF – Refers to a maritime radio specifically designed for use on boats. The Coast Guard monitors these frequencies for emergencies.
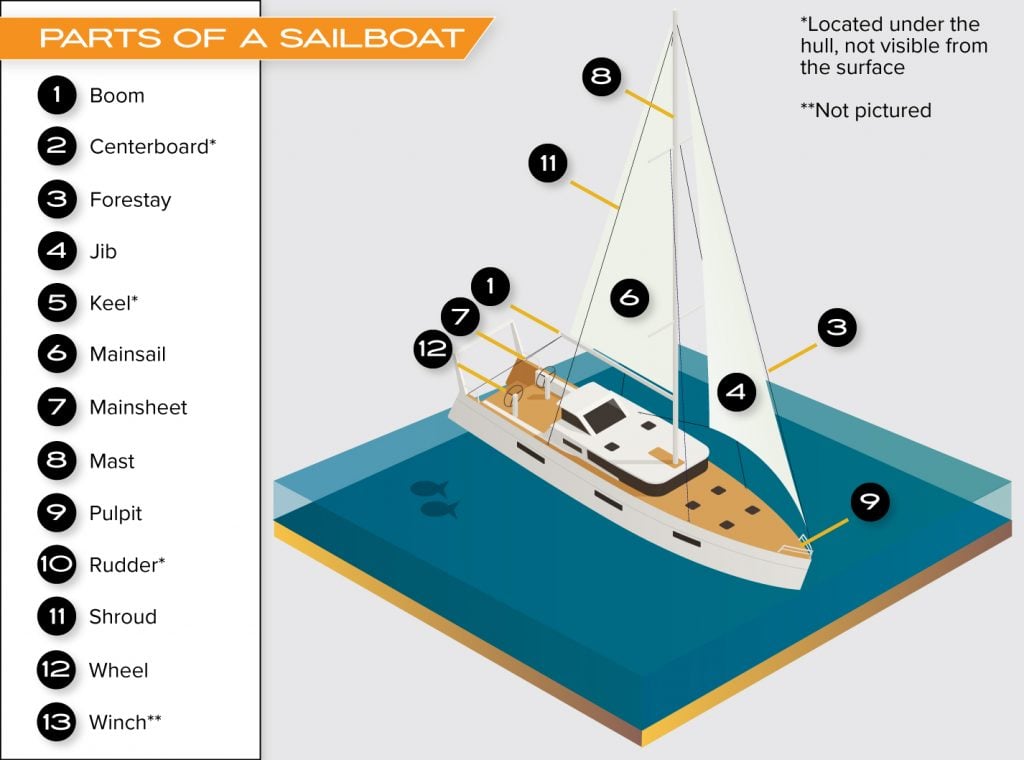
What are the Parts of a Sailboat?
In addition to the parts listed above, sailboats are outfitted with parts unique to sailing vessels.
- Boom – The boom is a horizontal spar that extends from the mast of a sailboat. Its primary purpose is to support the sails and keep them positioned correctly.
- Centerboard – A centerboard is a removable center fin attached to the bottom of a sailboat. The centerboard provides lateral resistance to wind and waves, allowing the boat to move more smoothly and efficiently through the water.
- Forestay – The forestay is a wire rope or rod that extends from the masthead to the bow of the vessel.
- Jib – A jib is a triangular sail attached to a sailboat’s forestay. The jib helps to propel the boat and is often used in conjunction with the mainsail.
- Keel – The keel of a sailboat is a long, thick piece of wood or metal that runs along the bottom of the hull. Its primary purpose is to provide stability and resistance to wind and waves.
- Mainsail – The mainsail is the primary sail on a sailboat located at the back of the boat. The mainsail attaches to the mast. It helps propel the boat through the water.
- Mainsheet – The mainsheet is a line that controls the mainsail on a sailboat. The mainsheet plays an important role in controlling the speed and direction of the boat and must be adjusted carefully in order to maximize performance.
- Mast – A mast is a tall vertical pole that supports the sails on a sailboat. The mast also supports the masthead, which is a platform at the top of the mast where navigation lights are mounted. The mast also serves as a mounting point for other equipment, such as radio antennas.
- Pulpit – A pulpit is a raised platform on the deck of a sailboat, typically near the bow, where someone can stand safely for observation or other purposes. Sailboats’ pulpit rails usually extend beyond the edge of the deck, providing extra safety for people on board.
- Rudder – A rudder is a flat piece of wood or metal attached to the back of a sailboat. It steers the boat by redirecting the water flowing past the rudder. A tiller steers the rudder. The tiller is a long pole that connects to the rudder.
- Shroud – The shroud is a large diameter line running from the masthead to the keel, used to support the mast laterally.
- Wheel – A wheel on a sailboat is a circular object that helps to steer the boat. It is usually located in the center of the boat and is operated by turning a wheel or handle in order to move the rudder.
- Winch – A winch is a mechanical device used to wind or unwind rope or cable. Winch systems are commonly used on sailboats to raise and lower the sails.
How Do Boats Move?
There are three main sources of power that move boats through the water.
The most basic way to move a boat is to use oars or paddles to row through the water. Paddling requires some effort on the part of the person paddling, but it is relatively simple and straightforward.
Wind is also another force used to propel boats. Sails are used to harness the power of the wind providing an effective and efficient way to move a boat.
Motors are also used to push boats through the water.
There are four main types of motors:
- Inboard Motor – An inboard motor is a type of boat engine mounted inside the vessel’s hull, in contrast to an outboard motor, which is mounted on the outside of the hull.
- Outboard Motor – An outboard motor is a propulsion system for boats, consisting of a self-contained unit that includes the engine, gearbox, and propeller, designed to be affixed to the outside of the transom.
- Sterndrive – A sterndrive is a type of engine mounted near the stern (back) of the boat. The engine is connected to the propeller via a long driveshaft that runs through the hull. Sterndrives are also referred to as inboard/outboard motors.
- Jet Drive – A jet drive is a propulsion system for boats. It uses a jet of water to push the boat forward. Jet drives are most commonly used in jet skis.
Final Word
Now that you know the parts of a boat, you’re ready to hit the open water. Whether you’re cruising around the lake or sailing across the sea, be sure to take time to appreciate all the hard work that went into building your vessel. And of course, don’t forget to enjoy the ride!
The post What are the Different Parts of a Boat Called? (A Complete Guide) appeared first on PartsVu Xchange.
